Home /
Expert Answers /
Biology /
which-of-the-following-statements-about-crossing-over-is-true-crossing-over-does-not-always-occur-pa573
(Solved): Which of the following statements about crossing over is TRUE? Crossing over does not always occur ...



Which of the following statements about crossing over is TRUE? Crossing over does not always occur to a tetrad. Crossing over occurs during Metaphase 1. Crossing over can occur between non-homologous chromosomes. Crossing over occurs in both mitosis and meiosis.
In meiosis, independent assortment lines up the chromatids in a single row along the cell's equator. randomizes which chromosomes end up in the daughter cells. changes the amount of DNA in gametes. alters the combinations of alleles that are found on a chromosome.
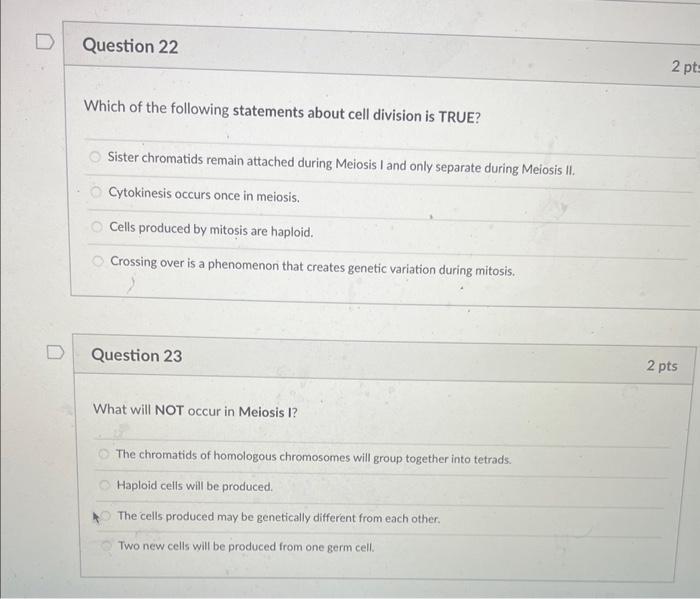
Which of the following statements about cell division is TRUE? Sister chromatids remain attached during Meiosis I and only separate during Meiosis II. Cytokinesis occurs once in meiosis. Cells produced by mitosis are haploid. Crossing over is a phenomenon that creates genetic variation during mitosis. Question 23 What will NOT occur in Meiosis I? The chromatids of homologous chromosomes will group together into tetrads. Haploid cells will be produced. The cells produced may be genetically different from each other. Two new cells will be produced from one germ cell.
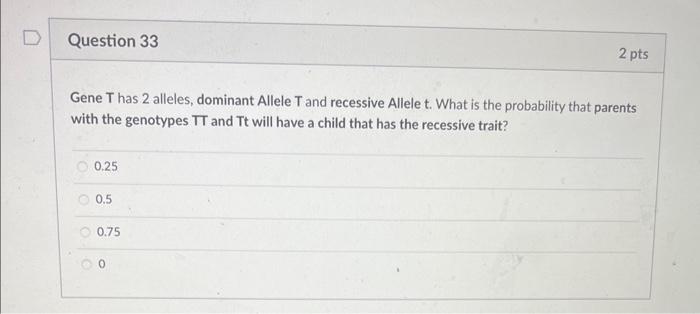
Gene \( \mathrm{T} \) has 2 alleles, dominant Allele \( \mathrm{T} \) and recessive Allele \( \mathrm{t} \). What is the probability that parents with the genotypes \( T \) and \( T t \) will have a child that has the recessive trait? \begin{tabular}{|c|} \hline \( 0.25 \) \\ \hline \( 0.5 \) \\ \hline \( 0.75 \) \\ \hline 0 \\ \hline \end{tabular}
Gene " \( G \) " and Gene "D" are located on different chromosomes. Allele \( G \) is dominant to allele \( g \), and allele \( \mathrm{D} \) is dominant to allele \( d \). What fraction of the offspring from the mating \( G g D d \times G g D d \) will be homozygous dominant for both genes? (Hint: you may want to do the Punnett square) \( 7 / 16 \) \( 1 / 16 \) \( 5 / 16 \) \( 3 / 16 \)
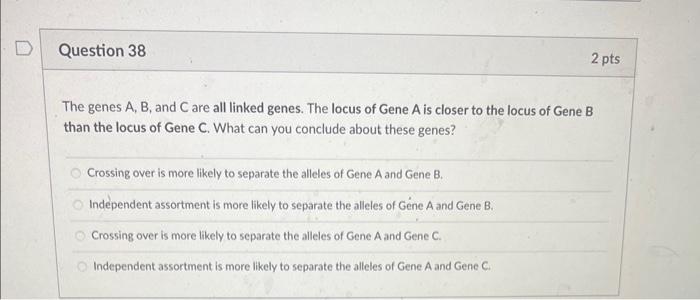
The genes A, B, and C are all linked genes. The locus of Gene A is closer to the locus of Gene B than the locus of Gene \( C \). What can you conclude about these genes? Crossing over is more likely to separate the alleles of Gene A and Gene B. Independent assortment is more likely to separate the alleles of Gene A and Gene B. Crossing over is more likely to separate the alleles of Gene A and Gene C. Independent assortment is more likely to separate the alleles of Gene A and Gene \( \mathrm{C} \).
Expert Answer
Answer - crossing over occurs during metaphasr -1 -