Home /
Expert Answers /
Advanced Physics /
the-roller-coaster-shown-in-the-figure-has-two-hills-two-dips-and-a-frictionless-track-at-the-tw-pa583
(Solved): The roller coaster shown in the figure has two hills, two dips, and a frictionless track. At the tw ...
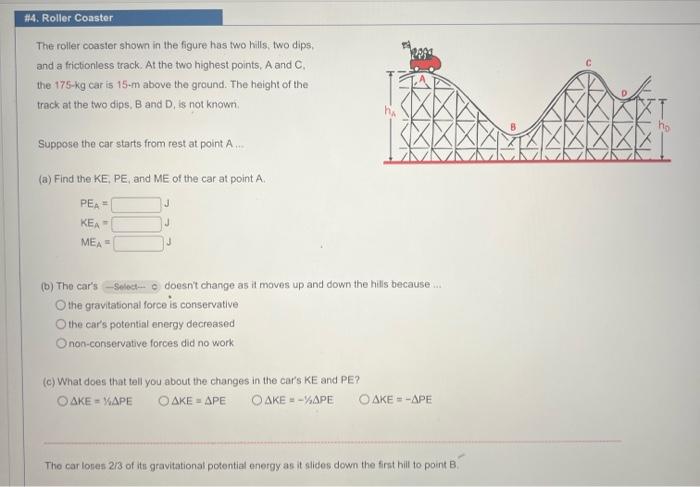
The roller coaster shown in the figure has two hills, two dips, and a frictionless track. At the two highest points, A and C. the \( 175-\mathrm{kg} \) car is 15-m above the ground. The height of the track at the two dips, \( B \) and \( D \), is not known. Suppose the car starts from rest at point A . (a) Find the KE, \( P E_{1} \) and ME of the car at point \( A \). (b) The car's doesn't change as it moves up and down the hills because ... the gravitational force is conservative the car's potential energy decreased non-conservative forces did no work (c) What does that tell you about the changes in the car's KE and PE? \[ \triangle K E=1 A P E \quad \triangle K E=\triangle P E \quad \Delta K E=-1 / A P E \quad \triangle K E=-\triangle P E \] The car loses \( 2 / 3 \) of its gravitational potential energy as it slides down the first hill to point B.
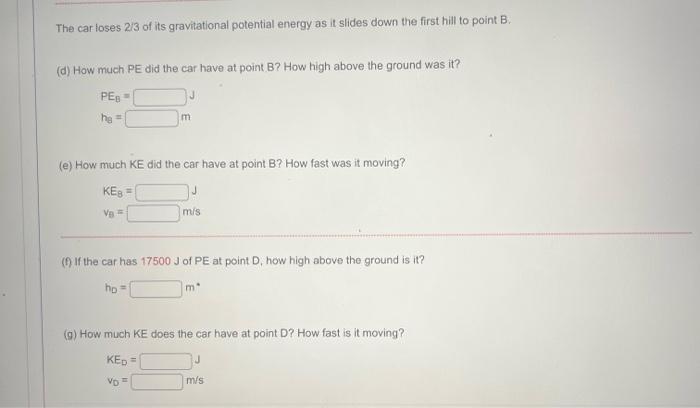
The car loses \( 2 / 3 \) of its gravitational potential energy as it slides down the first hill to point B. (d) How much PE did the car have at point B? How high above the ground was it? (e) How much KE did the car have at point B? How fast was it moving? \[ \begin{array}{ll} K_{8}= & J \\ v_{9}= & \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s} \end{array} \] (f) If the car has \( 17500 \mathrm{~J} \) of PE at point D, how high above the ground is it? \[ h_{D}=m^{*} \] (9) How much KE does the car have at point D? How fast is it moving?
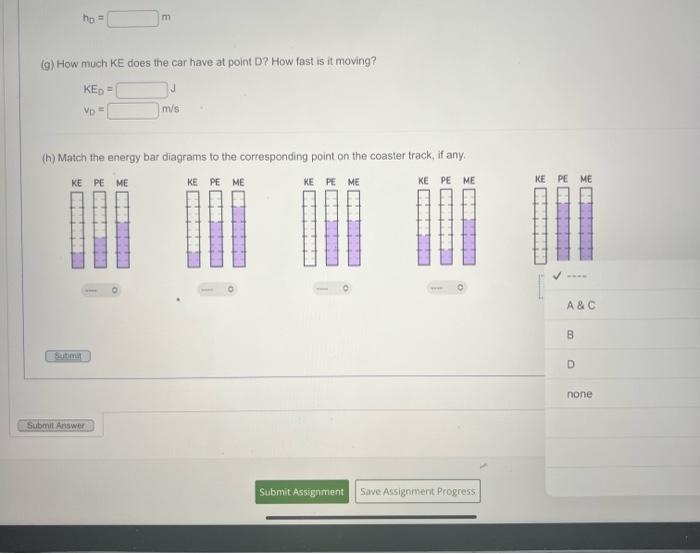
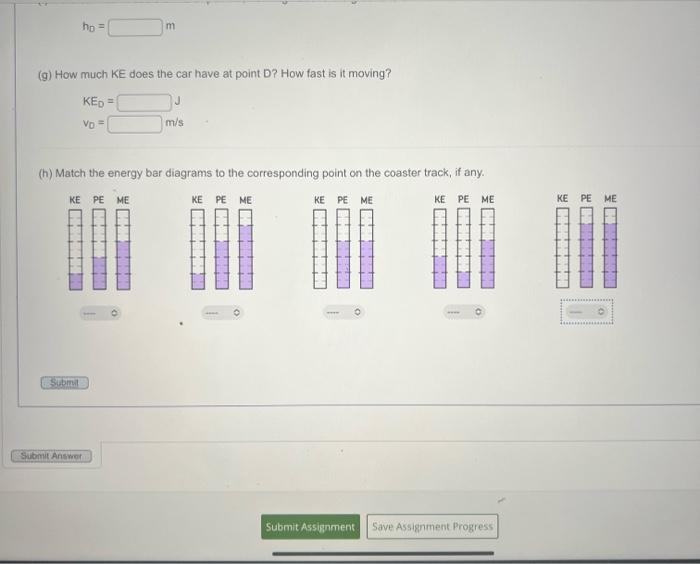
(g) How much KE does the car have at point D? How fast is it moving? \[ \begin{array}{ll} K_{D}= & J \\ v_{D}= & \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s} \end{array} \] (h) Match the energy bar diagrams to the corresponding point on the coaster track, if any.
(g) How much KE does the car have at point D? How fast is it moving? \[ \begin{array}{ll} K E_{0}= & \mathrm{J} \\ v_{0}= & \mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s} \end{array} \] (h) Match the energy ber diagrams to the corresponding point on the coaster track, if any.
Expert Answer
(a) The mass of the car is m=175 kg. The acceleration of gravity is g=9.8 m/s2. The height of the track at point A is hA=15 m. The potential energy of