Home /
Expert Answers /
Mechanical Engineering /
the-figures-are-just-the-area-mach-tables-nbsp-i-tried-posting-using-different-questions-per-che-pa415
(Solved): the figures are just the area mach tables I tried posting using different questions (per che ...
the figures are just the area mach tables
I tried posting using different questions (per chegg policy) but no one understands/ no luck.
Answer full question and I will upvote with two accounts.
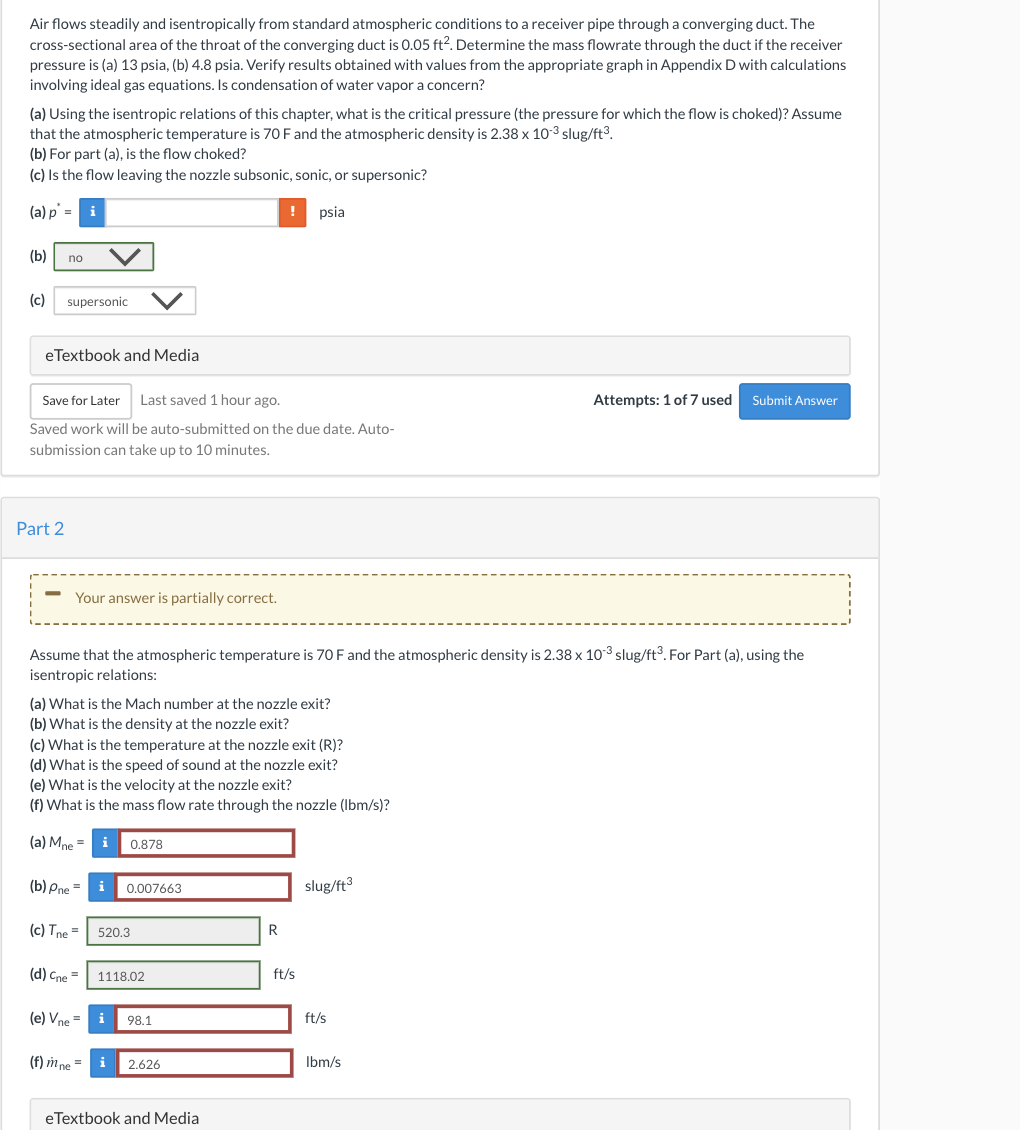
Air flows steadily and isentropically from standard atmospheric conditions to a receiver pipe through a converging duct. The cross-sectional area of the throat of the converging duct is \( 0.05 \mathrm{ft}^{2} \). Determine the mass flowrate through the duct if the receiver pressure is (a) 13 psia, (b) \( 4.8 \) psia. Verify results obtained with values from the appropriate graph in Appendix D with calculations involving ideal gas equations. Is condensation of water vapor a concern? (a) Using the isentropic relations of this chapter, what is the critical pressure (the pressure for which the flow is choked)? Assume that the atmospheric temperature is \( 70 \mathrm{~F} \) and the atmospheric density is \( 2.38 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{slug} / \mathrm{ft}^{3} \). (b) For part (a), is the flow choked? (c) Is the flow leaving the nozzle subsonic, sonic, or supersonic? (a) \( p^{*}= \) psia (b) (c) eTextbook and Media Last saved 1 hour ago. Attempts: 1 of 7 used Saved work will be auto-submitted on the due date. Auto- submission can take up to 10 minutes. Part 2 Assume that the atmospheric temperature is \( 70 \mathrm{~F} \) and the atmospheric density is \( 2.38 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{slug} / \mathrm{ft}^{3} \). For Part (a), using the isentropic relations: (a) What is the Mach number at the nozzle exit? (b) What is the density at the nozzle exit? (c) What is the temperature at the nozzle exit (R)? (d) What is the speed of sound at the nozzle exit? (e) What is the velocity at the nozzle exit? (f) What is the mass flow rate through the nozzle (Ibm/s)? (a) \( M_{\text {ne }}= \) (b) \( \rho_{\mathrm{ne}}= \) slug \( / \mathrm{ft}^{3} \) (c) \( T_{\mathrm{ne}}= \) R (d) \( c_{\mathrm{ne}}= \) \( \mathrm{ft} / \mathrm{s} \) (e) \( V_{n e}= \) \( \mathrm{ft} / \mathrm{s} \) (f) \( \dot{m}_{\mathrm{ne}}= \) \( \mathrm{lbm} / \mathrm{s} \)
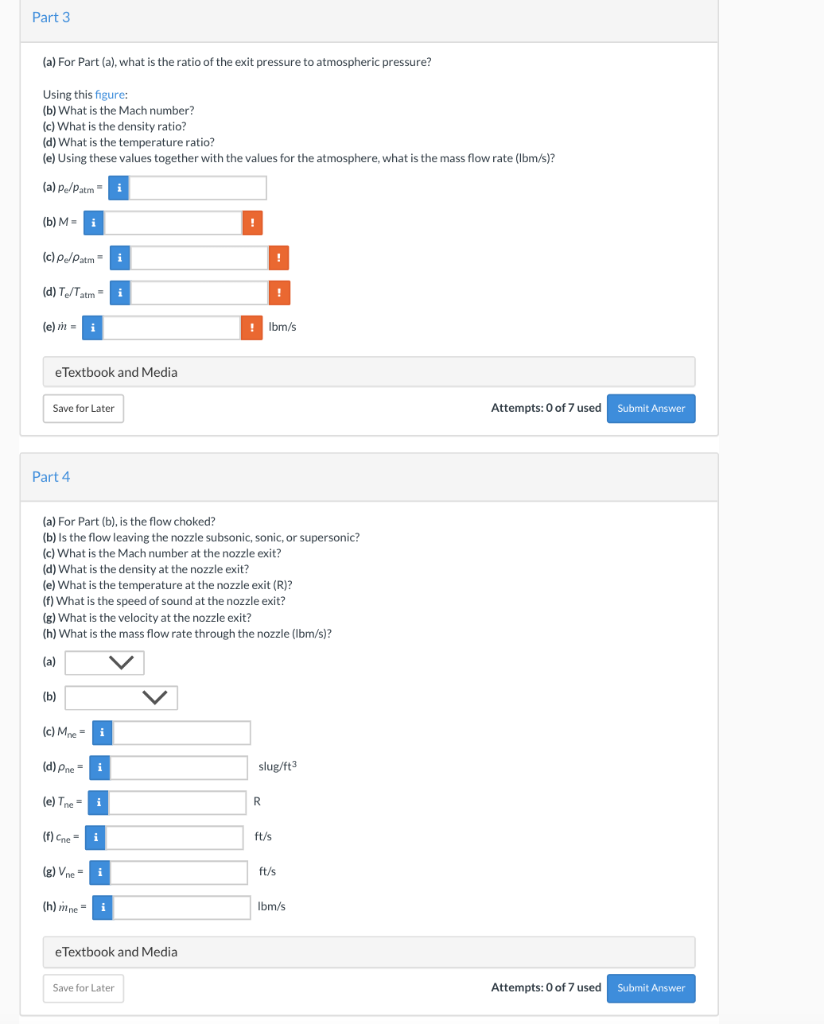
(a) For Part (a), what is the ratio of the exit pressure to atmospheric pressure? Using this figure: (b) What is the Mach number? (c) What is the density ratio? (d) What is the temperature ratio? (e) Using these values together with the values for the atmosphere, what is the mass flow rate (Ibm/s)? (a) \( p_{e} / p_{\text {atm }}= \) (b) \( M= \) (c) \( \rho_{e} / \rho_{a t m}= \) (d) \( T_{e} / T_{a t m}= \) (e) \( \dot{m}= \) \( \mathrm{lbm} / \mathrm{s} \) eTextbook and Media Attempts: 0 of 7 us: Part 4 (a) For Part (b), is the flow choked? (b) Is the flow leaving the nozzle subsonic, sonic, or supersonic? (c) What is the Mach number at the nozzle exit? (d) What is the density at the nozzle exit? (e) What is the temperature at the nozzle exit (R)? (f) What is the speed of sound at the nozzle exit? (g) What is the velocity at the nozzle exit? (h) What is the mass flow rate through the nozzle (Ibm/s)?