Home /
Expert Answers /
Mechanical Engineering /
the-figure-below-shows-a-vapor-power-cycle-that-provides-process-heat-and-produces-power-the-steam-pa565
(Solved): The figure below shows a vapor power cycle that provides process heat and produces power. The steam ...
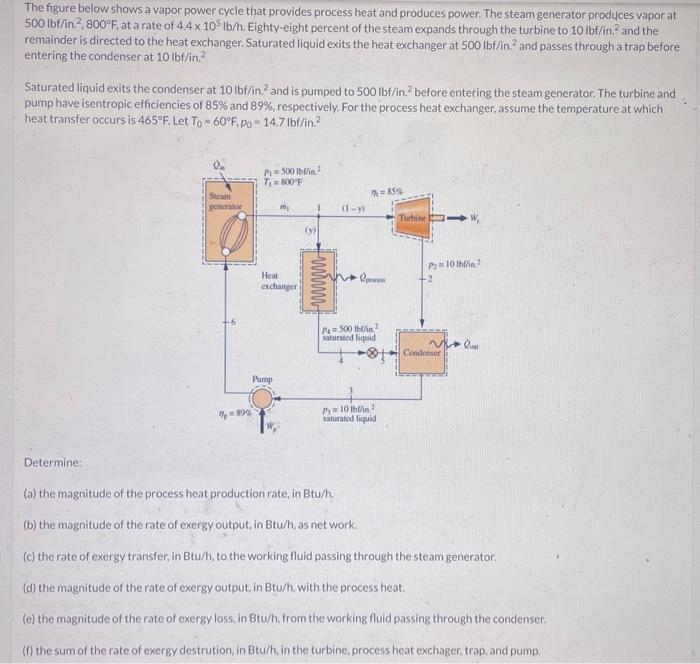
The figure below shows a vapor power cycle that provides process heat and produces power. The steam generator produces vapor at , at a rate of . Eighty-eight percent of the steam expands through the turbine to and the remainder is directed to the heat exchanger. Saturated liquid exits the heat exchanger at and passes through a trap before entering the condenser at Saturated liquid exits the condenser at and is pumped to before entering the steam generator. The turbine and pump have isentropic efficiencies of and , respectively. For the process heat exchanger, assume the temperature at which heat transfer occurs is . Let Determine: (a) the magnitude of the process heat production rate, in Btu/h. (b) the magnitude of the rate of exergy output, in Btu/h, as net work. (c) the rate of exergy transfer, in Btu/h, to the working fluid passing through the steam generator. (d) the magnitude of the rate of exergy output. in Btu/h. with the process heat. (e) the magnitude of the rate of exergy loss, in Btu/h, from the working fluid passing through the condenser. (f) the sum of the rate of exergy destrution, in Btu/h, in the turbine, process heat exchager, trap. and pump.