Home /
Expert Answers /
Accounting /
problem-6-2a-algo-calculate-ending-inventory-cost-of-goods-sold-sales-revenue-and-gross-profit-pa283
(Solved): Problem 6-2A (Algo) Calculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, sales revenue, and gross profit ...
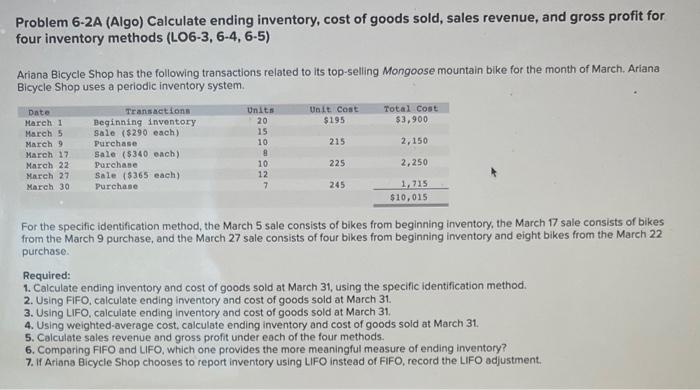
Problem 6-2A (Algo) Calculate ending inventory, cost of goods sold, sales revenue, and gross profit for four inventory methods (LO6-3, 6-4, 6-5) Ariana Bicycle Shop has the following transactions related to its top-selling Mongoose mountain bike for the month of March. Ariana Bicycle Shop uses a periodic inventory system. For the specific identification method, the March 5 sale consists of bikes from beginning inventory, the March 17 sale consists of bikes from the March 9 purchase, and the March 27 sale consists of four bikes from beginning inventory and eight bikes from the March 22 purchase. Required: 1. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31, using the specific identification method. 2. Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31. 3. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 . 4. Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31. 5. Calculate sales revenue and gross profit under each of the four methods. 6. Comparing FIFO and LIFO, which one provides the more meaningful measure of ending inventory? 7. If Ariana Bicycle Shop chooses to report inventory using LIFO instead of FiFO, record the LIFO adjustment.
from the March 9 purchase, and the March 27 sale consists of four bikes from beginning inventory and eight bikes from the Ma purchase. Required: 1. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31, using the specific identification method. 2. Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 . 3. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 . 4. Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31. 5. Calculate sales revenue and gross profit under each of the four methods. 6. Comparing FIFO and LIFO. Which one provides the more meaningful measure of ending inventory? 7. If Ariana Bicycle Shop chooses to report inventory using LIFO instead of FIFO, record the LIFO adjustment. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31, using the specific identification method.
Required: 1. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 , using the specific identification method. 2. Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 . 3. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31. 4. Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31. 5. Calculate sales revenue and gross profit under each of the four methods. 6. Comparing FIFO and LIFO, which one provides the more meaningful measure of ending inventory? 7. If Ariana Bicycle Shop chooses to report inventory using LIFO instead of FIFO, record the LIFO adjustment. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 .
Required: 1. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31, using the specific identification method. 2. Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31. 3. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 . 4. Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 . 5. Calculate sales revenue and gross profit under each of the four methods. 6. Comparing FIFO and LIFO, which one provides the more meaningful measure of ending inventory? 7. If Ariana Bicycle Shop chooses to report inventory using LIFO instead of FIFO, record the LIFO adjustment. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 .
Required: 1. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 , using the specific identification method. 2. Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31. 3. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31. 4. Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 , 5. Calculate sales revenue and gross profit under each of the four methods. 6. Comparing FIFO and LFFO, which one provides the more meaningful measure of ending inventory? 7. If Ariana Bicycle Shop chooses to report inventory using LIFO instead of FIFO, record the LIFO adjustment. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 . (Rounid your intermediate calculations to 4 decimal places and final answers to 2 decimal places.)
Requifed: 1. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31, using the specific identification method. 2. Using FIFO, calculate ending imventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 . 3. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 . 4. Using weighted-iverage cost, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31. 5. Calculate sales revenue and gross profit under each of the four methods. 6. Comparing FFFO and LLFO, Which one provides the more meaningful measure of ending inventory? 7. If Ariana Bicycle Shop chooses to report inventory using LIFO instead of FFO, record the LIFO adjustment. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Calculate sales revenue and gross proft under each of the four methods. (flound weighted-average unit cost amounts to 4 . decimal places.)
Required: 1. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31, using the specific identification method. 2. Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 . 3. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 . 4. Using weighted-average cost, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at March 31 . 5. Calculate sales revenue and gross profit under each of the four methods. 6. Comparing FIFO and LIFO, which one provides the more meaningful measure of ending inventory? 7. If Ariana Bicycle Shop chooses to report inventory using LIFO instead of FIFO, record the LIFO odjustment Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. If Ariana Bicyde Shop chooses to report inventory using LIFO instead of Fifo, record the LIFO adjustment. (If no entry is required for a transaction/event, select. "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.)
Expert Answer
Specific Identification Cost of goods available for sale Cost of goods sold Ending Inventory Unit Unit Cost Total Cost Unit Unit Cost Total Cost Unit