Home /
Expert Answers /
Chemistry /
please-answer-all-thank-you-nbsp-the-compound-shown-below-is-the-product-of-a-claisen-condensation-pa744
(Solved): please answer all thank you The compound shown below is the product of a Claisen condensation. ...
please answer all thank you
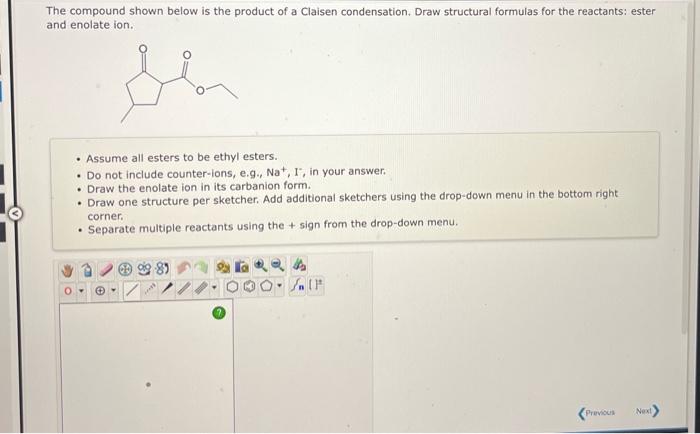







The compound shown below is the product of a Claisen condensation. Draw structural formulas for the reactants: ester and enolate ion. - Assume all esters to be ethyl esters. - Do not include counter-ions, e.g., \( \mathrm{Na}^{+}, \mathrm{I}^{-} \), in your answer. - Draw the enolate ion in its carbanion form. - Draw one structure per sketcher. Add additional sketchers using the drop-down menu in the bottom right corner. - Separate multiple reactants using the \( + \) sign from the drop-down menu.
The Michael reaction is a conjugate addition reaction between a stable nucleophilic enolate ion (the donor) and an a, \( \beta \) unsaturated carbonyl compound (the acceptor). Draw the structure of the product of the Michael reaction between ethyl propenoate and diethyl malonate. 9 more group attempte remaining
The Michael reaction is a conjugate addition reaction between a stable nucleophilic enolate ion (the donor) and an a, \( \beta \) unsaturated carbonyl compound (the acceptor). Draw the structure of the product of the Michael reaction between propenal and diethyl malonate.
This question has multiple parts. Work all the parts to get the most points. The Stork reaction is a condensation reaction between an enamine donor and an a, \( \beta \)-unsaturated carbonyl acceptor. The overall reaction consists of a three-step sequence of 1. formation of an enamine from a ketone, 2. Michael addition to an o, \( \beta \)-unsaturated carbonyl compound, and 3. hydrolysis of the enamine in dilute acid to regenerate the ketone. Consider the Stork reaction between cyclohexanone and ethyl propenoate. 1 Draw the structure of the product of the enamine formed between cyclohexanone and pyrrolidine.
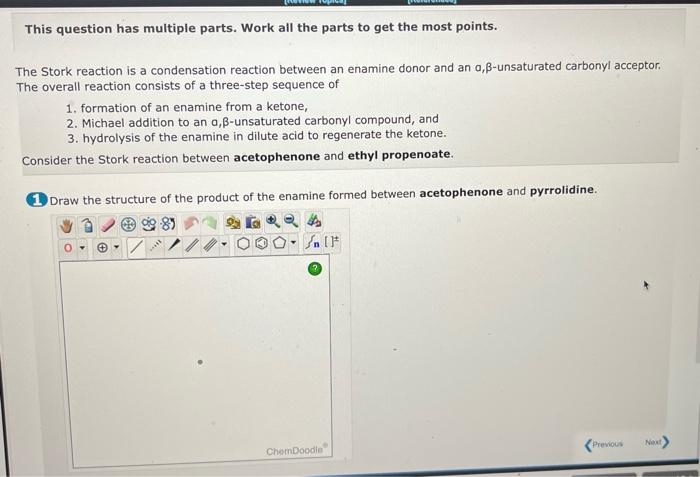
This question has multiple parts. Work all the parts to get the most points. The Stork reaction is a condensation reaction between an enamine donor and an \( \alpha, \beta \)-unsaturated carbonyl acceptor. The overall reaction consists of a three-step sequence of 1. formation of an enamine from a ketone, 2. Michael addition to an a, \( \beta \)-unsaturated carbonyl compound, and 3. hydrolysis of the enamine in dilute acid to regenerate the ketone. Consider the Stork reaction between acetophenone and ethyl propenoate. 1. Draw the structure of the product of the enamine formed between acetophenone and pyrrolidine.
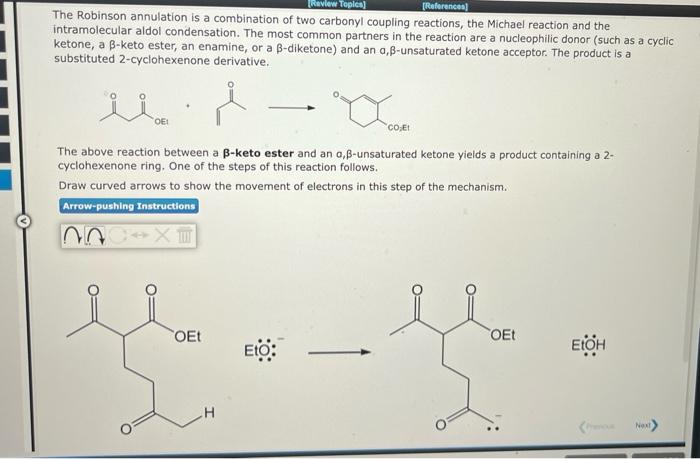
The Robinson annulation is a combination of two carbonyl coupling reactions, the Michael reaction and the intramolecular aldol condensation. The most common partners in the reaction are a nucleophilic donor (such as a cyclic ketone, a \( \beta \)-keto ester, an enamine, or a \( \beta \)-diketone) and an \( \alpha, \beta \)-unsaturated ketone acceptor. The product is a substituted 2-cyclohexenone derivative. The above reaction between a \( \beta \)-keto ester and an \( \alpha, \beta \)-unsaturated ketone yields a product containing a 2 cyclohexenone ring. One of the steps of this reaction follows. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism.
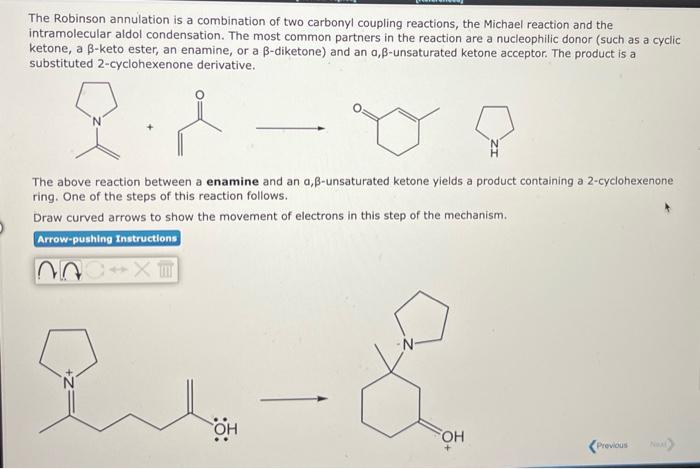
The Robinson annulation is a combination of two carbonyl coupling reactions, the Michael reaction and the intramolecular aldol condensation. The most common partners in the reaction are a nucleophilic donor (such as a cyclic ketone, a \( \beta \)-keto ester, an enamine, or a \( \beta \)-diketone) and an \( \alpha, \beta \)-unsaturated ketone acceptor. The product is a substituted 2-cyclohexenone derivative. The above reaction between a enamine and an \( \alpha, \beta \)-unsaturated ketone yields a product containing a 2 -cyclohexenone ring. One of the steps of this reaction follows. Draw curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in this step of the mechanism.