Home /
Expert Answers /
Electrical Engineering /
op-amp-based-circuits-25-marks-a-explain-cmrr-of-op-amp-with-relevant-circuit-and-equations-b-pa296
(Solved): Op-amp based circuits (25 Marks) a. Explain CMRR of op-amp with relevant circuit and equations. b. ...
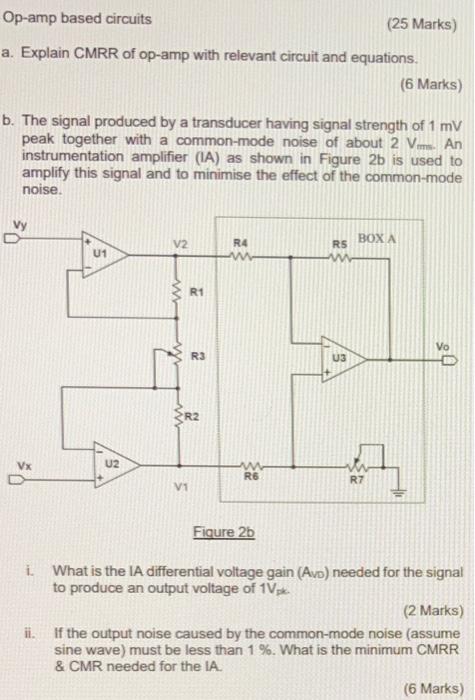

Op-amp based circuits (25 Marks) a. Explain CMRR of op-amp with relevant circuit and equations. b. The signal produced by a transducer having signal strength of 1 mV peak together with a common-mode noise of about 2 V. An instrumentation amplifier (IA) as shown in Figure 2b is used to amplify this signal and to minimise the effect of the common-mode noise. Vx U1 U2 V2 R1 V1 R3 R2 R4 w R6 Figure 2b RS U3 BOX A (6 Marks) R7 i. What is the IA differential voltage gain (Avo) needed for the signal to produce an output voltage of 1Vpk (2 Marks) ii. If the output noise caused by the common-mode noise (assume sine wave) must be less than 1%. What is the minimum CMRR & CMR needed for the IA. (6 Marks)
iii. Given that the voltage gain for the differential amplifier (BOX A) alone is 25, the overall IA gain is 1000, Given R4= R6=1k0, R?= R2, R7 Rs and R3 =10kQ. Calculate the resistors value for R? and Rs. iv. (4 Marks) Refer to the differential amplifier (BOX A), describe the purpose of using a trim-pot (potentiometer) for R7. (2 Marks) c. In regard to a practical op-amp performance. i. ii. What is meant by gain-bandwidth product of an op-amp? (2 Marks) An op-amp amplifier circuit has a closed-loop voltage gain of 5. If the op-amp used has a gain-bandwidth product of 1.5 MHz, and we can only tolerate 10% drop in gain, what will be the maximum usable frequency? (3 Marks)
Expert Answer
As par guidelines for multiple q only all subparts of any q should be solve here all parts of q.c is solved. c.(i) Gain bandwidth product of Op-Amp: The gain