Home /
Expert Answers /
Physics /
nbsp-figure-a-shows-the-basic-structure-of-a-human-eye-light-refracts-into-the-eye-through-t-pa236
(Solved): Figure (a) shows the basic structure of a human eye. Light refracts into the eye through t ...
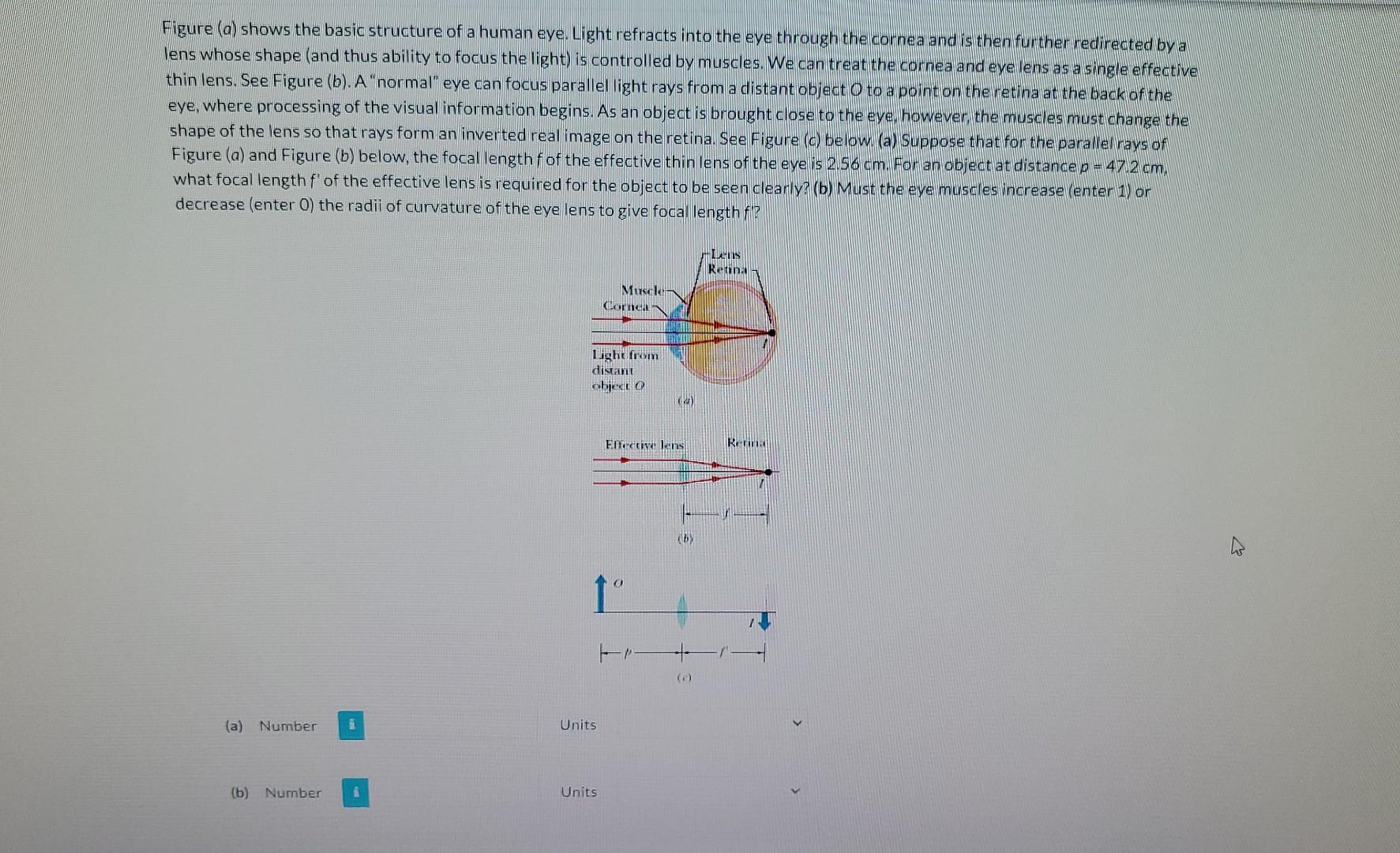
Figure (a) shows the basic structure of a human eye. Light refracts into the eye through the cornea and is then further redirected by a lens whose shape (and thus ability to focus the light) is controlled by muscles. We can treat the cornea and eye lens as a single effective thin lens. See Figure (b). A "normal" eye can focus parallel light rays from a distant object \( O \) to a point on the retina at the back of the eye, where processing of the visual information begins. As an object is brought close to the eye, however, the muscles must change the shape of the lens so that rays form an inverted real image on the retina. See Figure (c) below. (a) Suppose that for the parallel rays off Figure \( (a) \) and Figure \( (b) \) below, the focal length f of the effective thin lens of the eye is \( 2.56 \mathrm{~cm} \). For an object at distance \( p=47.2 \mathrm{~cm} \), what focal length \( f^{\prime} \) of the effective lens is required for the object to be seen clearly? (b) Must the eye muscles increase (enter 1 ) or decrease (enter 0 ) the radii of curvature of the eye lens to give focal length f'?
Expert Answer
in figure (a) and (b) the rays are coming from distant