Home /
Expert Answers /
Biology /
human-traits-exercise-introduction-analyses-of-human-traits-offer-genetic-examples-including-comple-pa457
(Solved): HUMAN TRAITS EXERCISE INTRODUCTION Analyses of human traits offer genetic examples including comple ...

HUMAN TRAITS EXERCISE INTRODUCTION Analyses of human traits offer genetic examples including complete dominance, incomplete dominance, codominance, and sex linkage. In this exercise you will examine the complexities and modes of inheritance of many human genetic traits. Monogenetic characteristies Analysis of human genetic characters is usually complex because many characters are influenced by multigene interactions and environmental factors. In this exercise we will concentrate on those charactenstics determined by variations of a single gene without much environmental influence. You should be able to determine the phenotype and make good inferences (if not precise) about the genotypes controlling the charncteristic. This will be particularly important when you analyze dominant phenotypes because you will not know by certain whether the second allele is also dominant or recessive for that particular characteristic under study. Some of these characteristics are discussed belowi Ability to taste Phenylthiocarbamide (PTC) Determined by a dominant allele T that seems to confer the ability to taste the chemical. Homozygous recessives for the allele lack the ability to taste PTC. In order to asses your tasting abilities, place a piece of control paper on your tongue and keep it there for at least 10 seconds. Then. place a piece of PTC paper in your mouth and keep it for 10 seconds. A distinct bitter taste will develop during this time if you are a taster. If you have to wonder if you taste or not, then you are a nontaster. Ability to roll tongue This characteristic is determined by a dominant gene \( R \), that gives some people the ability to roll the tongue into a chanacteristic U shape. Earlobes Atrached earlobes represent the homozygous recessive condition (gene \( \mathrm{f} \) ). Interlocking fingers Studies suggest that placing the left finger over the right when you cross your hand is due to a dominant gene L. Bent little finger Caused by a dominant gene B that causes the last joint of the little finger to bend inward toward the fourth finger. Lay your hands flat on the bench while relaxing the muscles to observe this phenotype. Widow's Peak Due to a dominant gene W, this shows in some people as a drop in the hairline downward fonning a distinct point at the center of the forehead. Examine your front hairline to detemine if you have this phenotype. Hitchhiker's thumb (distal hyperextensibility of the thumb) The expression of this trait is due to a recessive gene T with variable expressivity (only one th imb) with \( 5 \% \) reduction in penetrance.
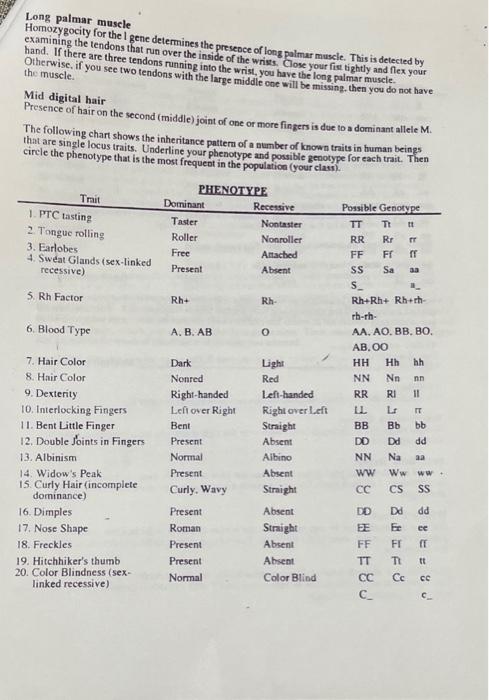
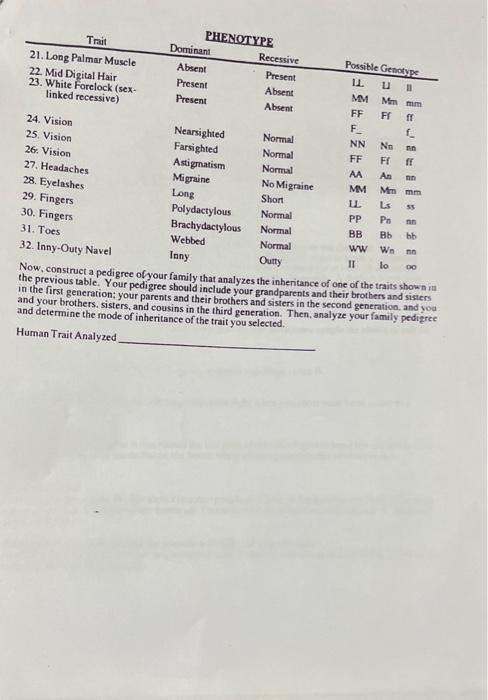
Long palmar muscle Hornozygocity for the l gene determines the presence of long palmar muscle. This is detected by examining the tendons that run over the inside of the wriss. Close your fier tightly and flex your hand. If there are three tendons running into the wrist, you have the long palmar muscle. Mid digital hair Presence of hair on the second (middle) joint of one or more fingers is due to a dominant allele \( M \). The following chart shows the inheritance pattem of a number of known traits in human beings that are single locus traits. Underline your phenotype and possible genotype for each trait. Then circle the phenotype that is the most frequent in the population (your clasi).
the previous table. Youre ofyour family that analyzes the inheritance of one of the traits shown in in the first generarion pedigree should include your grandparents and their brothers and sisters and your brothers, sisters, parents and their brothers and sisters in the second generation. and you and determine the mode of cousins in the third generation. Then, analyze your family pedigree Human Trait Analyzed