Home /
Expert Answers /
Earth Sciences /
guide-to-the-universe-astronomy-101-writing-8-exploration-3-mathrm-ch-3-textbook-unders-pa469
(Solved): Guide to the Universe: ASTRONOMY 101 Writing 8 Exploration \( 3-\mathrm{CH} .3 \) Textbook: Unders ...
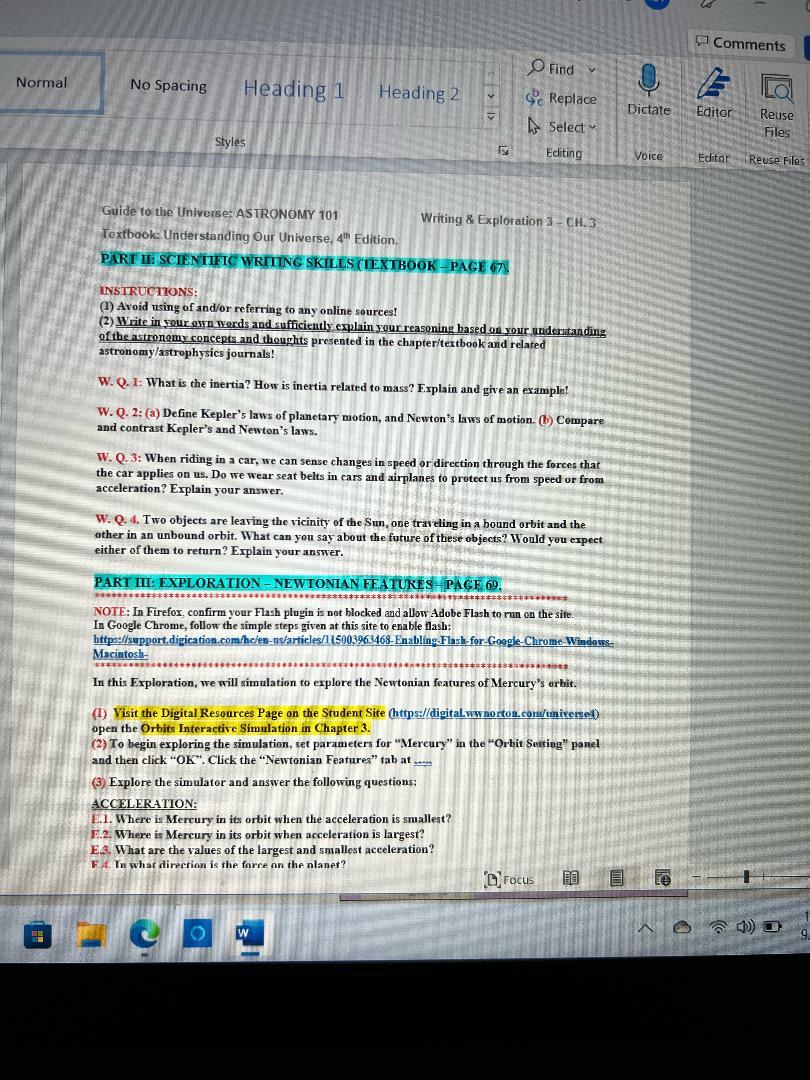
Guide to the Universe: ASTRONOMY 101 Writing 8 Exploration \( 3-\mathrm{CH} .3 \) Textbook: Understanding Our Universe, \( 4^{\text {th }} \) Edition. PARTII SCIENTIAC WRIIANG SKILLS (TEXTBOOK-PACE 67 . XNSTRUCTKONS: (1) Avoid using of and/or referring to any online sources! (2) Write in your ofrn werds and sufficiently explain your reasoning based or your understanding of the astronemy concepis and thoughts presented in the chapter/textbook and related astronomy/astrophysics journals! W. Q. 1: What is the inertia? How is inertia related to mass? Explain and give an example! W. Q. 2: (a) Define Kepler's laws of planetary motion, and Newton's laws of motion. (b) Cempare and contrast Kepler's and Newton's laws. W. Q.3: When riding in a car, we can sense changes in speed or direction through the forces that the car applies on us. Do we wear seat belts in cars and airplanes to protect us from speed or from acceleration? Explain your answer. W. Q. 4. Two objects are leaving the vicinity of the Sun, one traveling in a bound orbit and the other in an unbound orbit. What can you say about the future of these objects? Would you expect either of them to return? Explain your answer. PART III EXPLORATION - NEWTONIAN FE ATURES PACF 69 . NOTE: In Firefox, confirm your Flash plugin is not blocked and allow Adobe Flash to run on the site. In Google Chrome, follow the simple steps given at this site to enable flash: hitps://support,digication.comfhcien-ns/articles/115003963468-Enabling-Flash-for-Goggle-Chrome-WindonsMacintosh- In this Exploration, we will simulation to explore the Newtonian features of Mercury's erbit. (I) Visit the Digital Resources Page on the Student Site (https://digital.wWnorton.com/miversed) open the Orbits Interactive Simulation in Chapter 3 . (2) To begin exploring the simulation, set parameters for "Mereury" in the "Orbit Setting" panel and then click "OK". Click the "Newtonian Features" tab at .... (3) Explore the simulator and answer the following questions: ACCELERATION: E.1. Where is Mercury in its orbit when the acceleration is smallest? E.2. Where is Mercury in its orbit when acceleration is largest? E.8. What are the values of the largest and smallest acceleration? F. In what direction is the forre on the nlanet?
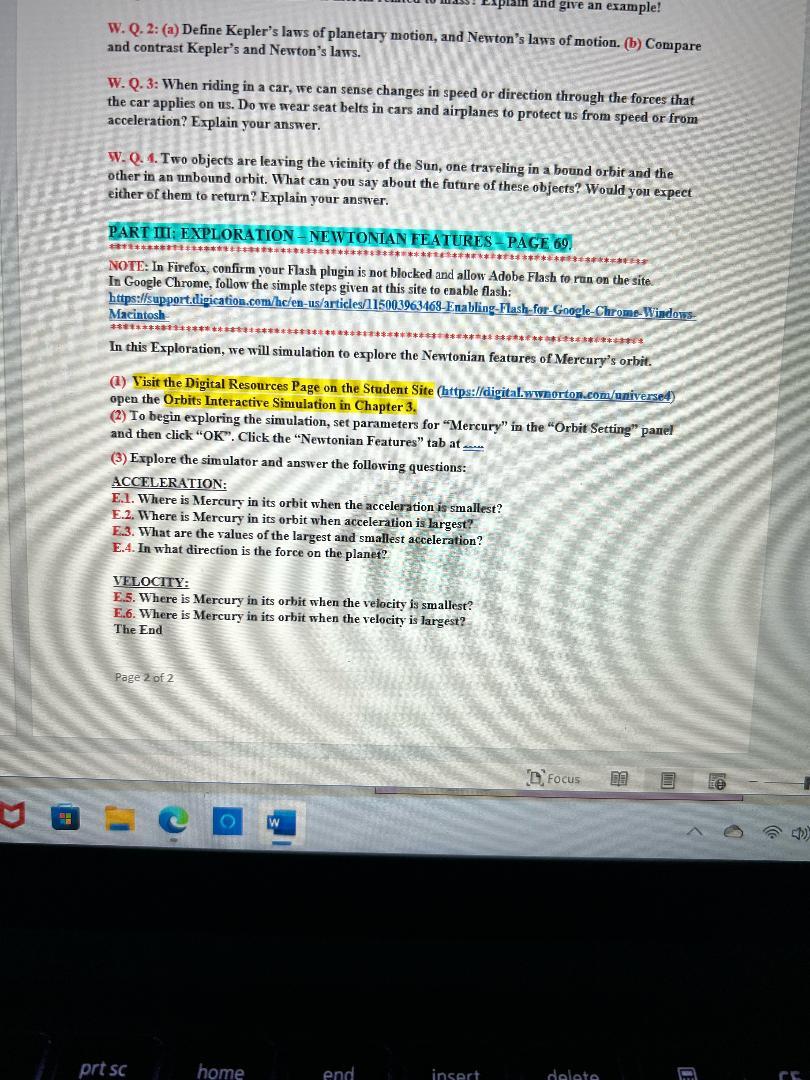
W. Q. 2: (a) Define Kepler's laws of planetary motion, and Newton's laws of motion. (b) Compare and contrast Kepler's and Newton's laws. W. Q.3: When riding in a car, we can sense changes in speed or direction through the forces that the car applies on us. Do we wear seat belts in cars and airplanes to protect us from speed or from acceleration? Explain your answer. W. Q. 4. Two objects are leaving the vicinity of the Sun, one traveling in a bound orbit and the other in an unbound orbit. What can you say about the future of these objects? Would you expect either of them to return? Explain your answer. PART III: EXPLORATION-NEWTONIAN FEATURES-PAGE 69. ********m: In Firefor, confirm your Flash plugin is not blocked and allow Adobe Flash to run on the site. NOTE: In Firefox, confirm your Flash plugin is not blocked and allow Adobe In Google Chrome, follow the simple steps given at this site to enable Alsh: In this Exploration, we will simulation to explore the Newtonian features of Mercury's orbit. (1) Visit the Digital Resources Page on the Stadent Site (https://digital.wwnortoncom/nniverse4) open the Orbits Interactive Simulation in Chapter 3 . (2) To begin exploring the simulation, set parameters for "Mercury" in the "Orbit Setting" panel and then click "OK". Click the "Newtonian Features" tab at .... (3) Explore the simulator and answer the following questions: ACCELERATION: E.1. Where is Mercury in its orbit when the acceleration is smallest? E.2. Where is Mercury in its orbit when acceleration is largest? E.3. What are the values of the largest and smallest acceleration? E.4. In what direction is the force on the planef? VELOCITY: E.5. Where is Mercury in its orbit when the velocity is smallest? E.6. Where is Mercury in its orbit when the velocity is largest? The End Page 2 of 2
Expert Answer
Solution:- Q 1)Ans:- Inertia is based upon on mass of an object and pressure as: Inertia and mass is predicated upon immediately on each distinct. Hen