Expert Answer
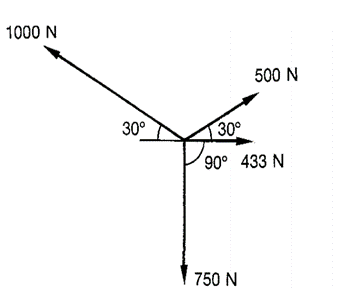
In physics, equilibrium refers to a state in which the net force and net torque acting on an object are both zero. In other words, the object is not accelerating and is either at rest or moving with constant velocity. When an object is in equilibrium, the forces acting on it are balanced.If we consider a situation where an object is in equilibrium, the sum of all the forces acting on the object must be zero. This is known as the equilibrium condition. So, in this context, the equilibrium force would be the resultant force that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the other forces acting on the object, in order to maintain equilibrium.