Home /
Expert Answers /
Electrical Engineering /
figure-13-1-see-figure-13-1-what-is-the-peak-to-peak-voltage-of-this-waveform-begin-arr-pa752
(Solved): Figure \( 13.1 \) See Figure 13.1. What is the peak-to-peak voltage of this waveform? \[ \begin{arr ...
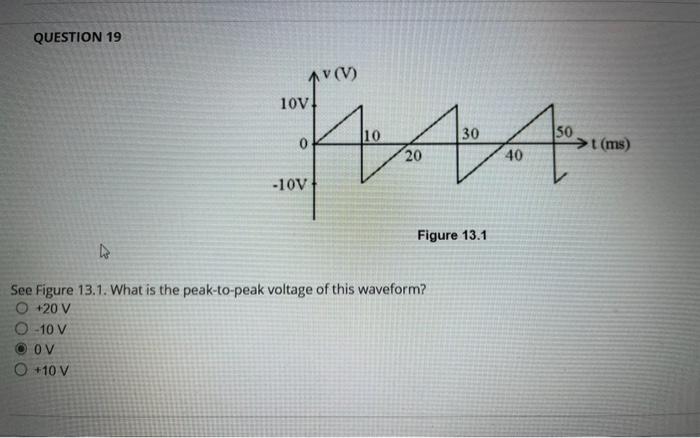
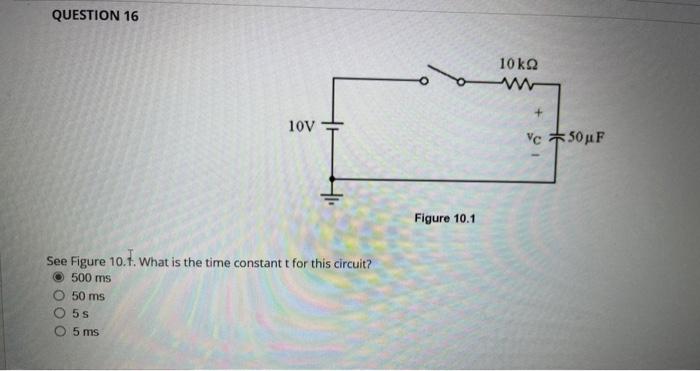


Figure \( 13.1 \) See Figure 13.1. What is the peak-to-peak voltage of this waveform? \[ \begin{array}{l} +20 \mathrm{~V} \\ -10 \mathrm{~V} \\ 0 \mathrm{~V} \\ +10 \mathrm{~V} \end{array} \]
Figure \( 10.1 \) See Figure 10.1. What is the time constant \( t \) for this circuit? \( 500 \mathrm{~ms} \) \( 50 \mathrm{~ms} \) \( 5 \mathrm{~s} \) \( 5 \mathrm{~ms} \)
Which of the fullowing is true of a series, open circuit? Source voltage and current will be read. Voltage and current will be equal. A voltage can be read, but current will be zero. A current can be read, but voltage will be zero.
Thevenin's theorem states that the Thevenin voltage is equal to short circuit voltage at the network terminals. open circuit voltage at the network terminals. short circuit current at the network terminals. open circuit current at the network terminals.
Thevenin's theorem states that you can replace a 2-terminal dc network with an equivalent circuit consisting of a current source and a parallel resistor. a voltage source and a parallel resistor. a voltage source and a series resistor. a current source and a series resistor.
Expert Answer
Given that, (19) Here given the Waveform with x-axis is Time and y-axi