(Solved): Detailed descriptions of Port Waikato rock types, from Jurassic basement through the Cenozoic lithol ...
Detailed descriptions of Port Waikato rock types, from Jurassic basement through the Cenozoic lithologies.
Background info:
The basement geology of New Zealand Port Waikato has settled on Jurassic basement(Mesozoic) it contains sandstone and siltstone with conglomerate and thin tuff beds and carbonaceous in places it’s Terrestrial is about carbonaceous sandstone, conglomerate and siltstone at top includes vegetation and coal seams. Several lithologies that ranges from Jurassic (Mesozoic) rocks to recent deposits can be discovered in the port Waikato region. The mainly rock type of Jurassic basement rocks is Murihiku Terrane rocks (greywacke) that are bordered to the north by the Waikato fault are the Jurassic basement rocks.
?Paleogeography of Late Eocene AWHI
to earliest Miocene Te Kuiti Group, central-western North Island?
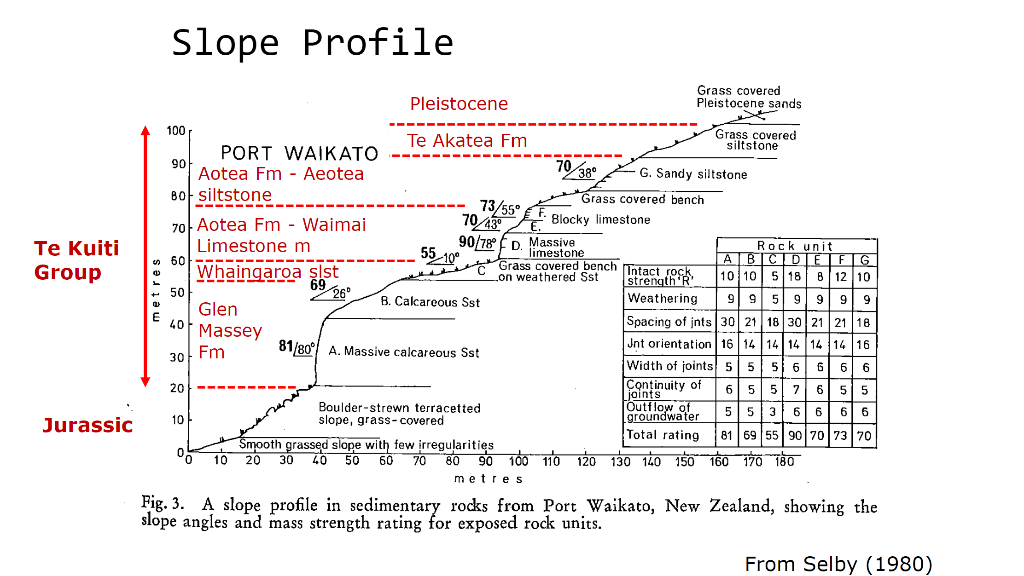
Huriwai Group which is from upper Jurassic age overlays the basement rocks. Materials from the tertiary period that belong to the Te Kuiti Group overlay the Upper Jurassic basement rocks and these sedimentary rocks are from the Oligocene age to the Lower Miocene age. In addition, sedimentary rocks from the Lower Miocene age that belong to the Waitemata Group overlays the Te Kuiti Group (in terms of the cliff lines around Auckland and the east coast base formation). Eventually, these rocks are then overlaid by the quaternary sediments. It also between the Waitemata group and the Pliocene deposits, there are also the sequences of Pliocene deposits. The Port dunes is from the Late Quaternary sediments which is in mobile and Modern fixed river dunes, there are locally paleosols and peat, loose and poorly consolidated. The Jurassic basement which is formed by the greywacke, also as known as the Murihiku Terrane rocks, has a 15 kilometers thickness and these significant basement deposits mainly contain the well stratified volcanic-derived sandstones, mudstones and a few conglomerates. They also form some large scale folding such as Waikato fault. The Huriwai group which is from the late Jurassic age contains siltstones, sandstones and conglomerates. The Jurassic is overlayed by the tertiary deposited, they are deposit from Oligocene to Lower Miocene sedimentary rocks which is from the Te Kuiti Group, the Te Akatea Siltstone is the youngest sedimentary rock, and the Aotea Formation is upon the Te Akatea Siltstone contains Waimai Limestone Member crystalline limestones, the Whaingaroa Siltstone is above and covered by Glen Massey Formation from early Oligocene 34~24 million years ago with Massive and bluff-forming sandstone and elgood Limestone Member. Waitemata Group is overlies the Te Kuiti Group from the early Miocene also the rock type dominated by calcareous sandstone and mudstone they usually have significant clay seams cause instability of landform and potential landslide. After the Waitemata Group is followed by Pliocene Kaawa Formation it’s the latest epoch in the Tertiary has slightly calcareous grey sorted carbonaceous sandstone with well sorted, non-calcareous yellow sands. Pliocene Kaawa Formation are overlayed by the Awhitu Group in sequence from Late Pliocene(5.3 million to 2.6 million years BP) to early Pleistocene contains Kaihu Sand from dune-bedding also the Pumiceous ignimbrite, Kidnappers Tephra, Brown-orange sands. On the top of all other sediments is Kaihu Group from Quaternary(2.5 million years ago) Kaihu Group contains Clayey pumiceous sands from Pleistocene also these fixed dune sand from the Holocene.
- . Insert your descriptions of Port Waikato virtual rock types, from Jurassic basement through the Cenozoic lithologies.
By showing the main rock types above
Briefly discuss the links between the weathering/erosional landscape and lithology types (relating surface expression to lithology). Use your understanding of lithology types to link to landscape units identified at Sunset Station (and the Waikawau Valley area). Refer to the slides contained in the Port Waikato Rock Samples file.
Expert Answer
The cover rocks incorporate areas of limestone that structure karst scenes close to Waitomo. Inland, the storm cellar rock formations are overlain by spasmodically saved Eocene to Late Miocene, mostly marine, sedimentary rocks of the Te Kuiti, Waitem