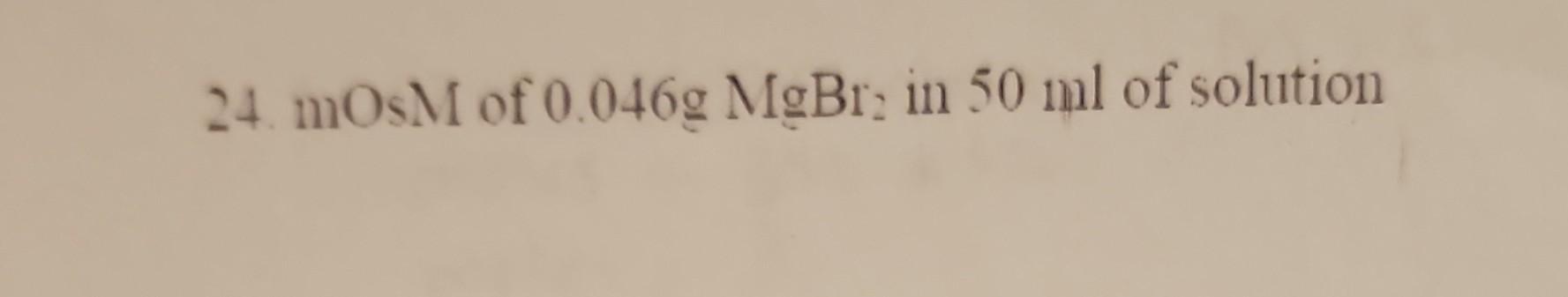Home /
Expert Answers /
Anatomy and Physiology /
calculate-the-osmolarity-million-molarity-osm-mosm-of-the-following-mosm-of-0-046g-mgbr2-in-50-m-pa181
Expert Answer
The number of osmoles (Osm) of solute per liter (L) of solution is known as osmolarity, which is a measure of solute concentration. The number of milliosmoles (mOsm) per liter is the definition of the more widely used milliosmolarity (mOsM) unit.One magnesium ion (Mg2+) and two bromide ions (Br-) separate out of the salt magnesium bromide (MgBr2) in solution. As a result, we obtain three osmoles of particle for every mole of MgBr2.The number of moles of solute must first be determined in order to determine the osmolarity of a solution. MgBr2 has a molar mass of about 184.11 g/mol (Mg has a mass of 24.31 g/mol and each of the two Br atoms has a mass of 79.9 g/mol). The steps to determine the osmolarity are as follows: 1. Calculate moles of MgBr2: