(Solved): Calculate Equivalent Units, Unit Costs, and Transferred CostsWeighted Average MethodCanfield Manu ...
Calculate Equivalent Units, Unit Costs, and Transferred Costs—Weighted Average Method
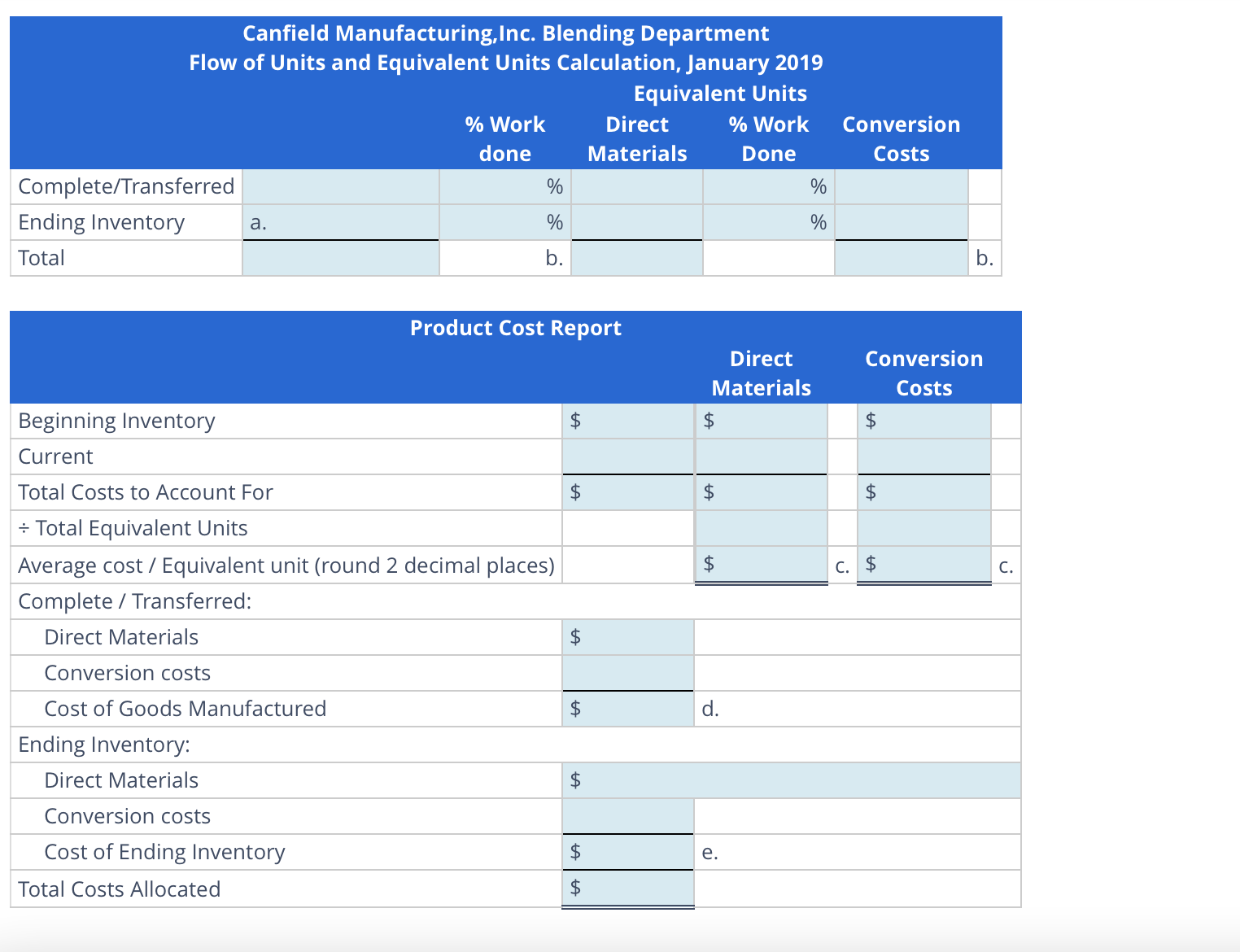
Canfield Manufacturing, Inc., operates a plant that produces its own regionally-marketed Spicy Steak Sauce. The sauce is produced in two processes, blending and bottling. In the Blending
Department, all materials are added at the start of the process, and labor and overhead are incurred evenly throughout the process. Canfield uses the weighted average method. The following data from the Work in Process—Blending Department account for January 2019 is missing a few items:
| Work in Process-Blending Department | |
|---|---|
| January 1 inventory (5,000 gallons, 60% processed) | |
| Direct material | $12,000 |
| Conversion costs | 5,900 |
| Transferred to Bottling Department (60,000 gallons) | |
| January charges: | |
| Direct material (61,000 gallons) | 153,000 |
| Direct labor | 73,600 |
| Manufacturing overhead | 42,480 |
| January 31 inventory [ ? gallons, 70% processed] | |
Required
Assuming Canfield uses the weighted average method in process costing, calculate the following amounts for the Blending Department:
Number of units in the January 31 inventory.
Equivalent units for materials and conversion costs.
January cost per equivalent unit for materials and conversion costs.
Cost of the units transferred to the Bottling Department.
Cost of the incomplete units in the January 31 inventory.
Round average cost per equivalent unit to two decimal places. Use rounded answers for subsequent calculations. Round other answers to the nearest whole number.