(Solved): A rail gun uses electromagnetic forces to accelerate a projectile to very high velocities. The basic ...
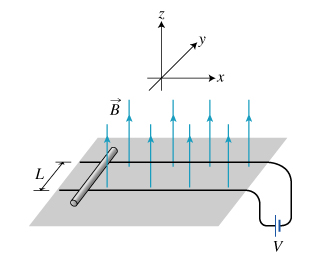
A rail gun uses electromagnetic forces to accelerate a projectile to very high velocities. The basic mechanism of acceleration is relatively simple and can be illustrated in the following example. A metal rod of mass 10.0 gg and electrical resistance 0.400 ΩΩ rests on parallel horizontal rails that have negligible electric resistance. The rails are a distance LL = 7.00 cmcm apart. (Figure 1)The rails are also connected to a voltage source providing a voltage of VV = 5.00 VV . The rod is placed in a vertical magnetic field. The rod begins to slide when the field reaches the value BB = 5.60×10−2 TT . Assume that the rod has a slightly flattened bottom so that it slides instead of rolling. Use 9.80 m/s2m/s2 for the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity. Figure 1 of 1 Part A Find μsμs, the coefficient of static friction between the rod and the rails. Give your answer numerically.