Home /
Expert Answers /
Biology /
1-in-chickens-the-shape-of-the-comb-is-determined-by-the-interaction-of-alleles-at-two-loci-a-pa275
(Solved): 1. In chickens, the shape of the comb is determined by the interaction of alleles at two loci, (A, ...






1. In chickens, the shape of the comb is determined by the interaction of alleles at two loci, (A, a and B, b). There are four possible comb shapes-walnut, rose, pea, and single. The walnut shape results from A_B_ genotype. Rose comb is produced from A_bb. Pea comb is produced from aaB_. Single comb is produced from aabb. For each of the following crosses, determine the phenotypes and proportions of each produced in the offspring. (6 × 2 = 12 marks) a. AABB x aabb b. AaBb x aabb c. AaBb × Aabb d. Aabb x Aabb e. Aabb x aaBb f. Aabb x aabb
2. A particular species of pea plant produces either purple or white flowers. A homozygous plant with purple flowers is crossed with a homozygous plant with white flowers. All F? offspring produced purple flowers. The F? were self- fertilized, and the following ratios in the F? were obtained: 9 purple: 7 white. a. Deduce the genotypes of the parental plants in this cross. (2 marks) b. Outline a possible biochemical pathway to account for the flower colour in this particular plant. (4 marks) 3. A particular plant which produces sickle shaped fruit is crossed with another variety which produces round fruit. All of the F? plants bear sickle shaped fruit. Upon self- fertilization of the F? plants, the following outcome is observed: 9/16 sickle shaped; 6/16 oblong shaped; 1/16 round fruit. Determine the genotypes of these F2 plants. (6 marks)
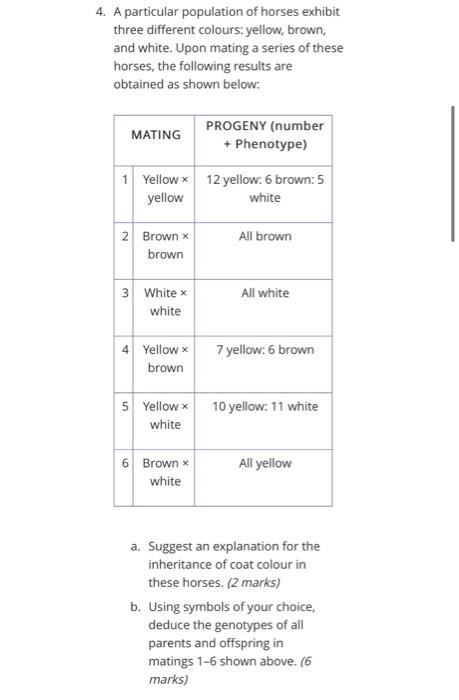
4. A particular population of horses exhibit three different colours: yellow, brown, and white. Upon mating a series of these horses, the following results are obtained as shown below: MATING 1 Yellow x 12 yellow: 6 brown: 5 yellow white 2 Brown x brown 3 White x white 4 Yellow x brown 5 Yellow x white PROGENY (number + Phenotype) 6 Brown x white All brown All white 7 yellow: 6 brown 10 yellow: 11 white All yellow a. Suggest an explanation for the inheritance of coat colour in these horses. (2 marks) b. Using symbols of your choice, deduce the genotypes of all parents and offspring in matings 1-6 shown above. (6 marks)
5. You are studying a particular gene which causes Ankylosing spondylitis, but you do not know which chromosome it is on. The following somatic-cell hybridization cell lines (F-J) is constructed. Using this information, determine which chromosome would the Ankylosing spondylitis gene be found. (4 marks) 6. Cell Line Gene Product Present 1 2 1 C H I Human Chromosome Present in Call Line a. If a series of four alleles exists in a given diploid (2n) species, how many alleles will be present in: (3 x 2 = 6 marks) i. A chromosome? ii. A pair of chromosomes? iii. An individual member of the species? b. How many genotypic combinations would occur in the entire species? (1 mark)
7. In a particular plant species, a particular locus on a chromosome is multi-allelic (bt, b¹, b² and b), whilst on another chromosome, two possible alleles can occur at a particular locus (c + and c). Calculate how many different genotypes with respect to these two sets of alleles can possibly occur in a particular population of this plant species. (2 marks)
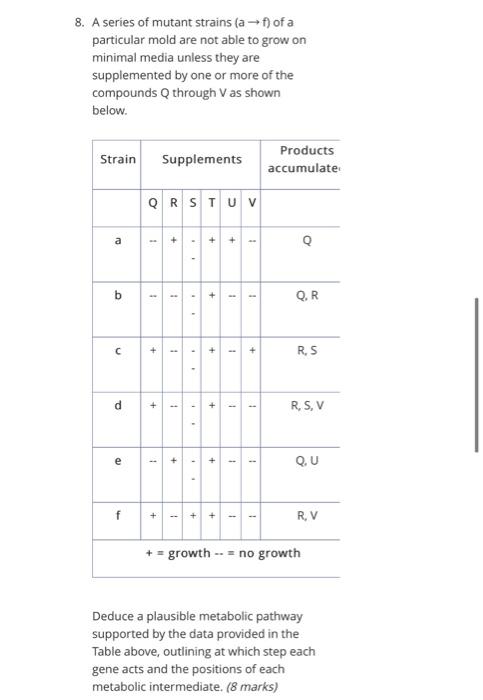
8. A series of mutant strains (af) of a particular mold are not able to grow on minimal media unless they are supplemented by one or more of the compounds Q through V as shown below. Strain a b ? d e f QRSTUV 1 1 + + 1 Supplements + T 1 1 1 + + + + + + + + + 1 1 1 1 1 1 + 1 Products accumulate Q.R R.S R, S, V Q.U R, V + = growth -- = no growth Deduce a plausible metabolic pathway supported by the data provided in the Table above, outlining at which step each gene acts and the positions of each metabolic intermediate. (8 marks)
9. In a particular plant, red pigment is produced from a colourless precursor through an enzymatic reaction. Purple pigment may be produced from the red pigment through hydroxylation via another enzyme. In a particular cross of two purple plants, the offspring produced were: 80 purple: 27 red: 37 white. a. Deduce how many gene pairs are involved in the production of colour in these plants. (2 marks) b. State the genotypes of the purple parents and of all the offspring produced in the cross above. (4 marks)
10. 200 cherry seeds were planted, all of which were derived from crosses of the same parents. The following describes the numbers and phenotypes of the trees produced: 12- yellow cherries, hairless stems 16- yellow cherries, very hairy stems 27-yellow cherries, patchy short haired stems 33- red cherries, very hairy stems 38 - red cherries, hairless stems 74 - red cherries, patchy short haired stems From this data, deduce the mode of inheritance of cherry colour and stem hairs, and state the genotypes of the parents and expected phenotypic ratios of the 200 offspring based on the mode of inheritance indicated. (6 marks)
Expert Answer
1) a) AABB x aabb Gametes produced by AABB = AB Gametes produced by aabb = ab F1:- AaBb (walnut-shape) Phenotypic ratio = 1 proportion of walnut-shape = 1 b) AaBb x aabb Gametes produced by AaBb = AB, Ab, aB, and ab Gametes produced by aabb = ab F1:-