Home /
Expert Answers /
Biology /
1-in-cases-of-ethylene-glycol-poisoning-and-its-characteristic-metabolic-acidosis-treatment-invol-pa582
(Solved): 1. In cases of ethylene glycol poisoning and its characteristic metabolic acidosis, treatment invol ...
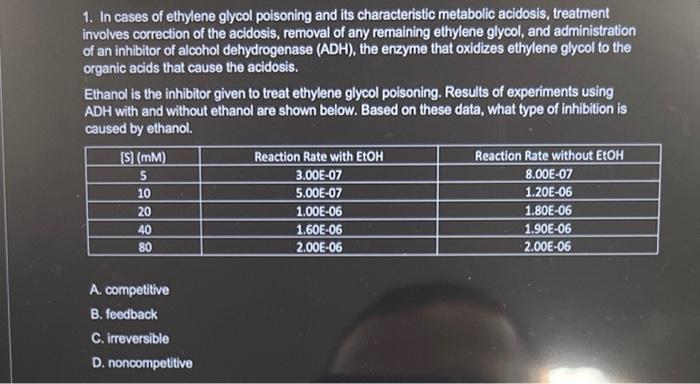

1. In cases of ethylene glycol poisoning and its characteristic metabolic acidosis, treatment involves correction of the acidosis, removal of any remaining ethylene glycol, and administration of an inhibitor of alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), the enzyme that oxidizes ethylene glycol to the organic acids that cause the acidosis. Ethanol is the inhibitor given to treat ethylene glycol poisoning. Results of experiments using ADH with and without ethanol are shown below. Based on these data, what type of inhibition is caused by ethanol. A. competitive B. feedback C. irreversible D. noncompetitive
2. ADH requires NAD+ for catalytic activity. In the reaction catalyzed by ADH, an alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde as NAD+ is reduced to NADH and dissociates from the enzyme. The \( \mathrm{NAD}+ \) is functioning as a/an: Also see the link for Enzymes: principles and biotechnological applications in the Week 4 folder.
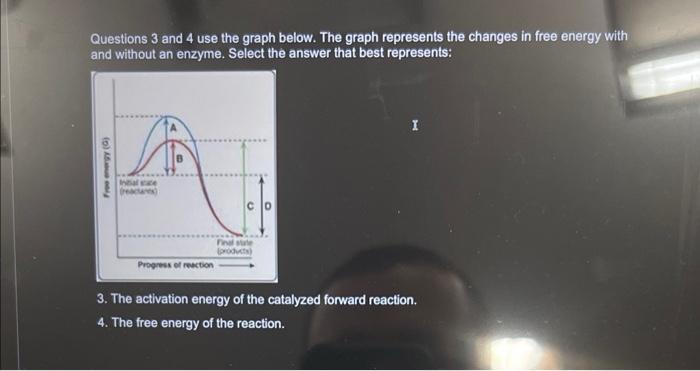
Questions 3 and 4 use the graph below. The graph represents the changes in free energy with and without an enzyme. Select the answer that best represents: \( \boldsymbol{I} \) 3. The activation energy of the catalyzed forward reaction. 4. The free energy of the reaction.
Expert Answer
Answer 1 :- A) Competitive Ethanol is beneficial for blocking physiological metabolism for et